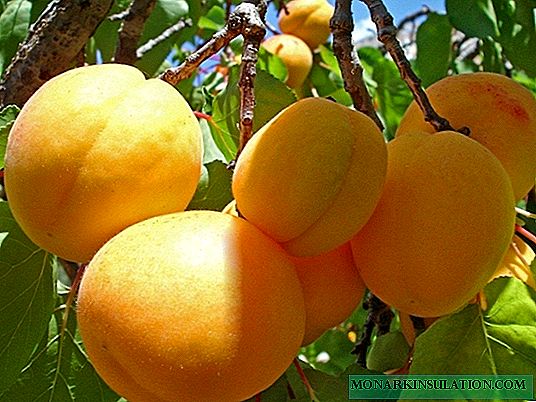
It is hard to imagine a garden without an apricot. Tasty, vitamin berry - traditionally is the basis of fragrant jams, preserves, compotes and dried apricots. When the gardener is faced with the task of planting an apricot of the sort on the plot, it would be useful to meet the Son of Krasnoshchek, a worthy descendant of his parent.
Description apricot varieties Son Krasnoshchekogo
From the name it is clear that this apricot is a direct descendant of the popular Krasnoshcheky variety. The second parent is Golden Summer apricot. The breeders, having registered the father of our hero in the State Register in 1947, immediately started working on the Son of the Krasnoshchekoy and in 1948 they transferred them to the state variety test. After 27 years, the variety was listed in the State Register for the Lower Volga region.
The tree turned out to be powerful, of medium height. The crown is raised, oval in shape. Branching inside the crown is average, not too thick, but the leaves are large and there are many.
It has good winter hardiness of wood withstanding thirty degrees of frost. But flower buds do not withstand return frosts, and when this happens, you can’t expect many fruits in the summer. Fortunately, this happens infrequently due to the late flowering inherent in this variety.
The grafted seedlings bring the first berries for 4-5 years from the moment of planting.
The variety is self-fertile, does not need pollinators. Undemanding to soils and care.
Harvest, directly dependent on the wintering of flower buds, averages 20 kg per tree, and in successful years - up to 30 kg.
The berries are slightly smaller than that of the father. The average weight is about 30 g. If the yield is normalized, cutting off a certain number of ovaries, then they grow to 50-60 g.
The color of the fruit is yellow, closer to orange. On the sunny side is a little blush. The skin is slightly covered with a soft fluff. The pulp is dense, juicy, sweet and very tasty. Light pleasant acid and subtle bitterness give the apricot a piquant taste.
The stone is large, easily detached, the core is bitter, unfit for food.

The stone of the apricot berry is the son of Krasnoshcheok large, easily detached
One of the strengths of the variety is its high resistance to moniliosis and kleasterosporiosis.
Landing rules
Planting an apricot Son of Krasnoshchekoy is no more difficult than another, you just need to follow the usual rules and sequence of actions.
- Choosing the right place to plant is the platform for the future life of the tree. The place where the apricot will grow must meet the following criteria:
- Well lit by the sun. Apricot will grow in the shade, but will not bloom.
- Be protected from cold winds. A good location will be if there is a fence, a house wall or thick trees from the north or northeast of the apricot. If this is not the case, for the first few years you will have to use specially made shields painted in white.
- Apricot grows well on the southern and southwestern slopes. The slope should not be large, up to 15 º - the best option.
- Since the tree of the Son of Krasnoshchek is large, he needs a lot of space. The distance to a neighboring tree in a row should not be less than four meters, and between rows not less than five meters.

The distance between adjacent apricot trees, the Son of Krasnoshchekoy, must be at least 4 meters, and between rows not less than 5 meters
- The apricot roots are prone to melting, so the tree will not grow on flooded, wetlands. Need a dry, elevated place.
- Timing for landing. It is recommended to do this in early spring before the start of sap flow. Seedlings planted at such a time better take root and they have a lot of time ahead to have time to take root and get stronger before the onset of winter. For seedlings with a closed root system, this principle is not critical - they can be planted during the growing season.
- The acquisition of seedlings is planned for the fall. Preference when choosing should be given to one or two year old seedlings. At this age, plants tolerate transplanting better and take root more quickly. When buying, you should pay attention to the state of the root system - it must be well developed and possess fibrous roots.
- The sapling is laid for winter storage in the basement with an air temperature of 0-5 ºС. The roots are placed in a humid environment (wet sand or sawdust), after dipping in a mash of red clay and mullein. You can store the seedling dug in the ground. To do this, prepare a pit of a suitable size. A layer of sand is poured to the bottom, a seedling is laid obliquely, the roots are covered with sand and watered. Then they completely cover the pit with earth, and in winter they cover it with a layer of snow up to 60 cm high. In early spring, snow is scooped up so that the seedling does not spill.
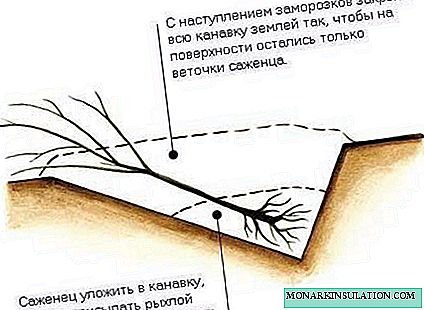
If there is no suitable basement, the seedling can be dug.
- Before the onset of winter, they prepare a landing pit in the following order:
- At the chosen place they dig a hole. If the top layer consists of chernozem rich in humus, it is laid aside for future use. The size of the pit should be sufficient to accommodate the root system and the supply of the nutrient mixture (usually the diameter and depth are 70-80 cm).
- A drainage layer of crushed stone, gravel, expanded clay or other similar materials is laid at the bottom. Layer thickness - 10 - 15 cm.
- The nutrient mixture, which consists of equal parts of chernozem, organic matter, peat and sand, is filled up. Mineral fertilizers are added - 300-400 g of superphosphate and 1.5 liters of wood ash. Mix well with a shovel or pitchfork. Cover with a film or roofing material to prevent leaching of nutrients.

A nutrient mixture is poured into the landing pit, consisting of equal parts of chernozem, organic matter, peat and sand
- In the spring, when the time comes, they take out a seedling from the shelter. After making sure that he wintered safely, the roots are soaked in water for 1-2 hours. You can add growth stimulants and root formation, for example, Kornevin, Epin and the like.
- A hole is opened and a small mound of nutrient mixture is made. At a distance of 10-15 cm from the center, a wooden stake is driven in, not less than 1.5 times the height of the seedling.
- The root neck of the seedling is placed on the top of the knoll, the roots are carefully straightened and laid. The root neck should be slightly deepened (3-5 cm) so that after sedimentation of the soil it does not come to the surface.
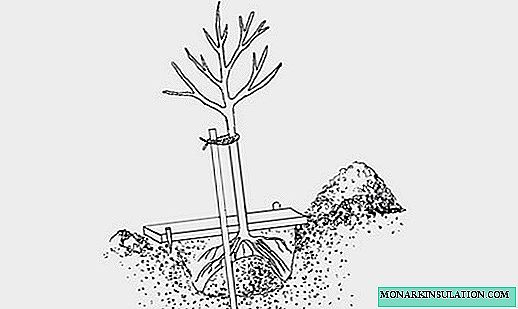
The root neck of the seedling is located on the top of the knoll and is deepened by 3-5 cm
- They fill the pit with earth, tamping well in layers.
- Tie a sapling with soft material (tape, rope), trying not to pass the trunk.
- Around the plant form a near-trunk circle. It is convenient to do this with a chopper or a plane cutter.
- Abundantly watered with water. The roots should get good contact with the soil, no sinuses should remain around them.

The seedling is abundantly watered.
- They mulch with suitable material - humus, compost, rotted sawdust, etc.
- The first stage of forming pruning is carried out - the central conductor and side branches are shortened by 30-40%. Remember to grease the surface of the slices with garden var.
When buying a garden var, you should pay attention to the composition. The plant will not benefit from the presence of petroleum products in it (gasoline, kerosene, petrolatum, etc.). The best compounds are based on natural ingredients - beeswax, lanolin.
Video: apricot planting rules
Features of cultivation and subtleties of care
Apricot The son of the Red-cheeked needs the usual care for this culture for proper growth and fruiting. Types and methods of measures to ensure the vital functions of this plant are known and available to an experienced gardener. It is useful for a beginner to get to know them briefly.
Table: apricot care types Son of the Red Cheek
| Type of care | Deadlines | How to perform |
| Watering |
| The soil is moistened to a depth of 30-40 cm, in the fall - 60 cm |
| The application of organic fertilizers (humus, compost) | First time the next year after harvest, then once every three years | Close up in the soil when digging in the fall or in the spring at the rate of 5 kg / m2 |
| The introduction of nitrogen-containing fertilizers (urea, ammonium nitrate) | Annually in spring | For digging, evenly sprinkle on the ground at the rate of 30-40 g / m2 |
| Application of potash fertilizers (potassium monophosphate, potassium sulfate) | Annually during fruit growth | Combine with watering, dissolving in a bucket of water 10-20 g of fertilizer (normal for 1 m2) |
| The application of phosphorus-containing fertilizers (superphosphate, double superphosphate) | Annually in autumn | For digging, evenly sprinkle on the ground at the rate of 20-30g / m2 |
| Application of liquid top dressing to improve fruiting | In the summer, during the period of growth and ripening of fruits | Prepare infusions from
The selected infusion is kept in a warm place for 5-10 days and watered, previously diluted with water in a ratio of one to ten. |
| Complex fertilizers | According to instructions | |
| Forming Cut | Proceed at the time of landing and spend in early spring for 4-5 years | Give the crown a sparse-tiered form |
| Sanitary pruning | Annually in early late fall or early spring | Dry, diseased and damaged branches are cut |
| Adjust cropping | Combine with sanitary | It is carried out if necessary, if the crown is thickened |
| Anti-aging pruning | Early spring, if necessary | Carried out in two ways:
|
Diseases and Pests
By combining the ability of the variety to resist moniliosis and kleasterosporiosis with the regular implementation of preventive work, the gardener will not encounter problems associated with diseases and pests of apricot.
The main preventive measures are carried out in the autumn as part of the preparation of the garden for winter, some are performed at other times of the year.
Table: measures for the prevention of diseases and pests of apricot
| Type of work | Deadlines | Notes |
| Collection and disposal of fallen leaves | Autumn | Branches and leaves removed during pruning are burned. The resulting ash is used as fertilizer. |
| Sanitary pruning | Late fall, early spring | |
| Scraping and crack treatment | Fall spring | If there are cracks on the bark, they are peeled to a healthy bark, disinfected with 1% solution of copper sulfate and covered with garden var |
| Lime whitewash of boles and skeletal branches | Autumn | The solution for whitewashing is prepared from slaked lime, adding 1% copper sulfate |
| Digging trunk trunks | Autumn | |
| Protecting young trees from possible frost | Late fall | If winters in the region are severe, young trees (up to 3-4 years old) need to be insulated. This can be done using a frame made of wooden bars or poles, covered with a film or covering material. |
| Processing crown with 3% solution of copper sulfate | Late fall, early spring | Copper sulfate can be replaced with iron sulfate with a concentration of 5% |
| Treatment with complex preparations for diseases and pests | Early spring | The following drugs are used that are effective against all fungi and insects:
|
| Systemic fungicide treatment | After flowering with an interval of 2-3 weeks | Apply drugs with a short waiting period, such as Horus, Quadris. Processing is completed 7 days before eating berries. |
Possible diseases
In case the apricot is still ill, you need to know the signs and nature of the course of the main probable diseases.
Kleasterosporiosis (perforated spotting)
A fungal disease that appears in the spring on the leaves of a plant. Subsequently, it can go on shoots and fruits. When fungal spores get on the leaves, small red-brown spots first appear. Rapidly developing, the fungus expands the spots to sizes of 5-10 mm. The inside dries up and gets enough sleep, holes with a reddish fringing form. If the weather is wet, it takes 10-15 days. Regular treatment with fungicides, as indicated in the table above, does not allow the disease to spread. If this is not done, then the disease will quickly cover the entire plant and in August all the leaves will fall off.

The inside of the spots dries out and gets enough sleep, forming holes
Moniliosis (monilial burn)
Spores of the causative agent of this disease usually fall on the apricot during flowering. Bees, collecting nectar, carry along with the pollen spores of the pathogen. Once inside the flower, the fungus first affects it, and then through the pestle penetrates further into the shoot and leaves. Such a lesion looks like a burn, which is the reason for the second name of the disease. If signs of moniliosis are found, first you need to cut the affected shoots, capturing at least 30 cm of healthy wood. Then you should start treatment with fungicides, conducting them at least three times with an interval of 2-3 weeks.

When the apricot leaves are affected by moniliosis, they wither and dry out
When infected in the summer, the fruits are affected. It looks like gray rot. The affected fruits are harvested and destroyed, the tree is treated with systemic fungicides with a short waiting time (Horus, Quadris).
Cytosporosis
This disease appears in the presence of open cracks on the tree bark, in which the fungus settles. With the development of the disease, the bark is destroyed, abundant gumming begins. Treatment consists in cleaning the affected areas of the cortex to healthy tissues, followed by disinfection with 1% solution of copper sulfate, treatment with fungicides. Then the lesion site is covered with a layer of garden var.

With the development of cytosporosis, the cortex is destroyed, abundant gumming begins
Possible pests
Apricot has few pests. Having noticed their appearance, the attentive gardener will quickly get rid of uninvited guests, using insecticides, for example, Fufanon, Decis.
Weevil beetle
A beautiful, small bug with a long proboscis. Winters in cracks of the bark, fallen leaves and topsoil under the crown. With the onset of spring, when the soil begins to warm up, the weevil wakes up from hibernation and begins to move up to the crown. If there is no calcareous whitewash and (or) hunting belt on the way, the beetle safely gets to the first food - swelling kidneys. If they are not stopped, flowers, leaves, ovaries and young shoots will follow.

Weevil eats buds, flowers, leaves, young shoots
At this time, you can collect the beetles manually. Early in the morning, until the air warms up and the temperature rises above 5 ºС, weevils sit numb and motionless on the branches. You just need to spread a cloth or film under the tree and shake them off the branches.
At the same time, insecticides are being treated, they will help get rid of the remaining pests.
Khrushchev
So called the larvae of various beetles, including weevils. In the latter they are small, only 4-6 mm. Maybug larvae are 20–25 mm in size. They crawl out of the eggs laid by bugs in early June. They cause significant damage to the roots of young trees. The main method of control is soil treatment with Diazonin. The drug is effective for three weeks, this is enough to destroy the gross. Diazonin does not accumulate in the soil and does not enter the fruit.

Khrushchev - beetle larva, crawls out of an egg in early summer, feeds on plant roots
Aphid
You can notice the attack of these small sucking pests by folded leaves. If you expand such a leaf, you can see in it small black, green - and there are other colors - insects. This is the aphid. Settling on leaves and young shoots, she eats them and gives off a sticky sweet liquid, so beloved by ants. To provide themselves with dessert, ants plant aphids on trees - if they are not stopped by hunting belts - and settle on leaves.They destroy the pest with insecticides, for example, Decis or Fufanon. Twisted leaves are pre-cut off, since when spraying the drug does not get inside.

Aphids settle on the inside of leaves
Grade Reviews
"Son of Krasnoshchekoy" is one of the most popular varieties suitable for cultivation in the suburbs and to the south. The winter hardiness of the variety is above average. The fruits are large, golden-orange in color. The pulp is dense, juicy, aromatic.
Svetlana170
//cottage71.ru/viewtopic.php?f=57&t=356//yagodka.club/frukty/abrikos-syin-krasnoshhekogo-opisanie-sorta-foto.html#hcq=WlmJLHq
The easiest way to distinguish the fruits of the variety Krasnoshchekoy from the variety Son red-cheeked on the kernel of the bone. In Krasnoshchekoy it is sweet, and in SK it is bitter.
Winegrower
//forum.vinograd.info/showthread.php?t=11246%20//yagodka.club/frukty/abrikos-syin-krasnoshhekogo-opisanie-sorta-foto.html#hcq=00dKLHq
But Krasnoshchek and the Son of Krasnoshchekoy, I grew well, but there was very little apricot, just frosts during the flowering period, very beautiful, bright, but .... And they removed it.
Volgograd, Nadezhda
//www.tomat-pomidor.com/newforum/index.php?topic=51.0%20//yagodka.club/frukty/abrikos-syin-krasnoshhekogo-opisanie-sorta-foto.html#hcq=b08LLHq
Apricot varieties Son of Krasnoshchekoy, having inherited the best qualities from his father, surpassed berries in taste, winter hardiness and disease resistance. Disadvantages - lower productivity and smaller berry size - a small fee for the undeniable advantages. The variety has been recognized by gardeners not only in the Lower Volga region - it is gradually moving north, and is also found in the Moscow Region. Due to its unpretentiousness to soil and care, it can be recommended for cultivation even by beginner gardeners.
















